brainstem auditory evoked potential
What is BAEP (Brainstem Auditory Evoked Potential)?
A brainstem auditory evoked potential (BAEP) is an evoked potential triggered by an aural stimulus. Electrodes placed on the scalp record reactions to noises, which are subsequently shown on an electroencephalogram (EEG). Responses to acoustic stimuli are generated by relay structures in the brainstem. If you have been experiencing changes in your hearing abilities that may be linked to difficulties with a specific nerve route, your doctor may advise you to get a BAEP test.
What does the BAEP detect?
A neurologist can determine the time it takes for an auditory stimulus to go from the point in the inner ear where the physical sound is transformed into a bioelectrical impulse to the brainstem using the BAEP. The neurologist can determine if the auditory nerve is working correctly based on these measurements. For example, an acoustic neuroma (a benign tumour of the ear canal) may stretch or compress the auditory nerve, causing it to take a lengthy time to interpret aural stimuli.
How to Get Ready for a BAEP Exam?
- The night before the test, wash your hair.
- On the day of the test, eat normal food and take your regular medications as usual.
- If you wear a hearing aid or have noticeable hearing issues, inform the person conducting the exam.
Procedure:
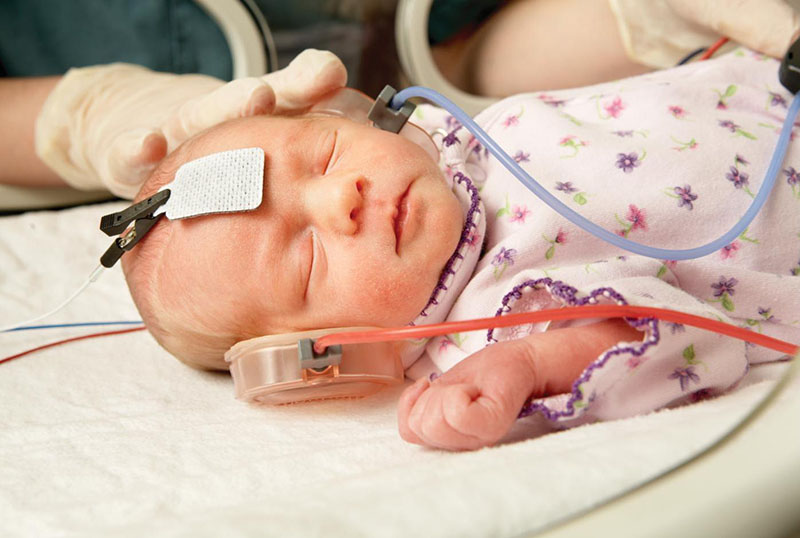
- Some electrodes will be applied to specific areas of your scalp or earlobe.
- You will be provided with specialized headphones or earplugs to wear.
- Then, using headphones, you will listen to a sequence of ‘clicks.
- Responses to clicks are recorded using specific equipment via the electrodes.
- The electrodes will be removed from your head after the treatment.
- After the test findings have been analysed, your doctor will discuss them with you regarding the treatment.
Are there any side effects with this BAEP test?
The BAEP testing technique is painless, and adverse effects are quite uncommon. There is a potential that the electrodes may cause slight skin discomfort. Patients are usually able to return home the same day once the procedure is completed.
What conditions are diagnosed by the BAEP TEST
- Hearing loss: Even if it is not complete, it can be detected as this causes the BAEP to change
- Acoustic Neuroma: a benign tumor of the hearing canal that may stretch or compress the auditory nerve, potentially leading to complications.
- Multiple sclerosis (MS): Patients with MS might have an aberrant BAEP even if there are no indications or symptoms of brainstem dysfunction.
- Subarachnoid Inflammation: induced by subarachnoid hemorrhage, meningitis, or Guillain-Barre syndrome.
- An aberrant BAEP has been linked to several neurological illnesses such as Friedreich’s ataxia, inherited cerebellar ataxia, and B2 deficiency.
What is the clinical use of the BAEP test?
- The BAEP may provide information about people who may have multiple sclerosis or other auditory nerve system abnormalities.
- BAEP monitoring is also used to evaluate a patient’s state during neurosurgical procedure and sometimes in the intensive care unit (ICU).
- BAEP testing is often less expensive than other methods such as MRI.
Is the BAEP test safe?
The BAEP method itself is non-invasive and safe.
For more information & consultation on Brainstem Auditory Evoked Potential Test, Call our expert Dr. Amit Shah – Consultant Neurologist in Mumbai on 98195 61456 or Book an Appointment