Digital EEG
What is EEG?
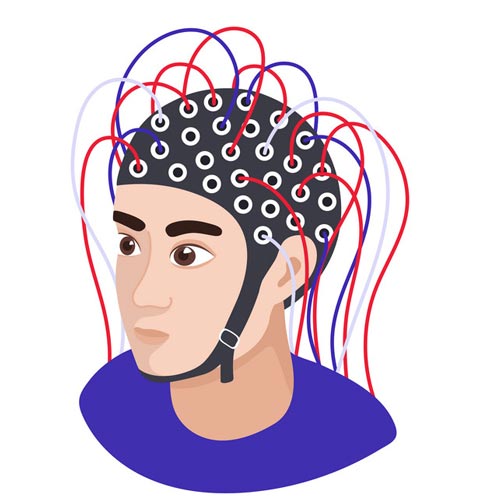
The electrical activity of the brain is evaluated using an EEG. It is a non-invasive monitoring tool that captures the patterns of electric impulses used by brain cells to interact with one another. EEG employs the use of small sensors known as electrodes, which are placed on the scalp. Wires attach these electrodes to an EEG recording equipment. The electrodes monitor the brain waves and send the data to a computer, which records the findings.
Brain wave EEG records resemble a wavy line with rises and falls. Doctors may spot irregularities in brain wave patterns by analyzing these recordings, which aids in the diagnosis of brain and sleep problems, including epilepsy. EEG is used to identify abnormalities in brain activity that may be linked to certain brain disorders. EEG may aid in the diagnosis of a variety of conditions, including epilepsy, sleep problems, and brain tumors.
What are the different types of EEG?
- Routine EEG: These might take anything from 30 minutes to an hour. You may be instructed to take deep breaths, look at a flashing light, or open and shut your eyes.
- Sleep-deprived EEG: When we are sleeping or awake, the electrical activity in our brains differs. In a sleep-deprived EEG, you will be instructed not to sleep the night before the test in order to increase your chances of falling asleep throughout the day. This implies that the psychologist may examine your brain’s electrical patterns as you sleep.
- Ambulatory EEG: A standard EEG may be insufficient to identify epilepsy. You wear an EEG helmet for a few hours or days at a time during an ambulatory EEG. This increases the chances that the EEG will capture while you are experiencing a seizure.
How is EEG performed?
There will be little or no discomfort during the process since EEG is non-invasive and painless. It is performed by a neurologist and normally takes 1 hour to complete the test process. The EEG test protocol is outlined below:
The patient will be instructed to lie on the exam table at first. The doctor next measures the head and marks the locations of the electrodes.
Electrodes are put on the designated indications with the assistance of a glue-like substance and wired to the machine, which records the impulses.
The data picked up by the electrodes that indicate the electrical activity of the brain are presented on the computer screen as wavy lines.
During the test, the doctor may instruct the patient to breathe fast and slowly or to look at a flashing light in order to examine changes in brain wave patterns.
When the test is finished, the doctor will remove the electrodes and wipe away the gel that was used to keep them in place.
What are the advantages of EEG?
- They are a very rapid, relatively inexpensive, and safe method of testing the functioning of several brain regions.
- Accurate time measurements
- Today’s EEG equipment can detect brain activity with a resolution of one millisecond.
- EEG electrodes simply adhere to the scalp. As a result, it is a non-invasive process.
- In comparison to other technologies, EEG equipment is generally affordable and easy to use.
For more information & consultation on EEG Test, Call our expert Dr. Amit Shah – Consultant Neurologist in Mumbai on 98195 61456 or Book an Appointment